Software Engineering Methods
Software Modelling & git
TI3115TU -- 2024-09-17Learning Objectives
- Understand ideas behind different workflows
- Apply tools to help with standardisation
- Understand and reflect on code quality
- Take part in constructive code reviews
Who has mocked around with git?
Who had issues?
Any questions?
Today
- Collaboration
- Code quality
- Standardisation
Homework
- Who has attempted it?
- Any general comments or quesitons?
1. Authentication
What's the default branch?
What is the HEAD pointing at?
How many working trees are accessible?
2. Adding commits
Working tree - staging - commit
Authorship and authentication
git - branching
Way to seperate prallel actions
branching strategies
Using branches to support team's workflow
There is no "standard"-way
branching strategies
Conventions: project specific, agreed-upon standrads
- Onboarding
- Misunderstanding
- Reduce conflicts (technical/social)
- Example: variable naming (e.g. camelCase, snake_case)
branching strategies: how to pick
- always integrate
- gather and release
Emma Westby: "determine release strategy first!"
Mark: "Pick the simplest one. Adapt if needed"
branching strategies: mainline development
"Trunk based" development
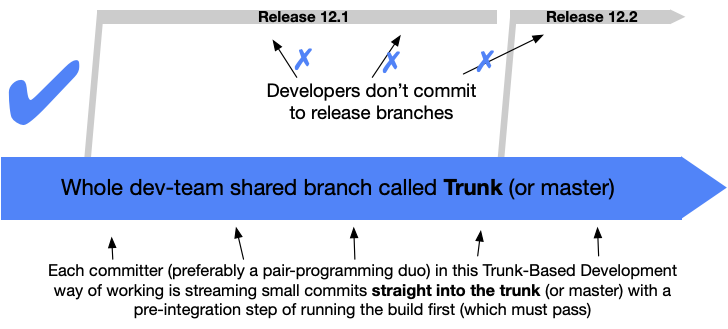
branching strategies: mainline development
"Trunk based" development at scale
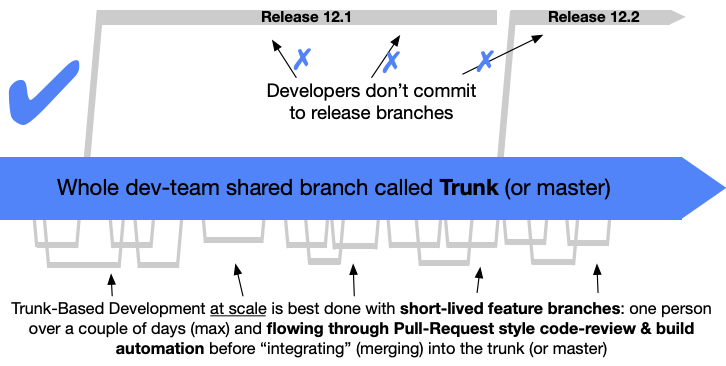
branching strategies: mainline development
Downsides?
Breaking changes introduce non-working trunk
Requires "always integrate" approach
Requires high level of trust
branching strategies: mainline development
Advantages?
Breaking fast and early
Small changes
Facilitates continous deployment
branching strategies: feature branches
"GitHub Flow" uses feature branches
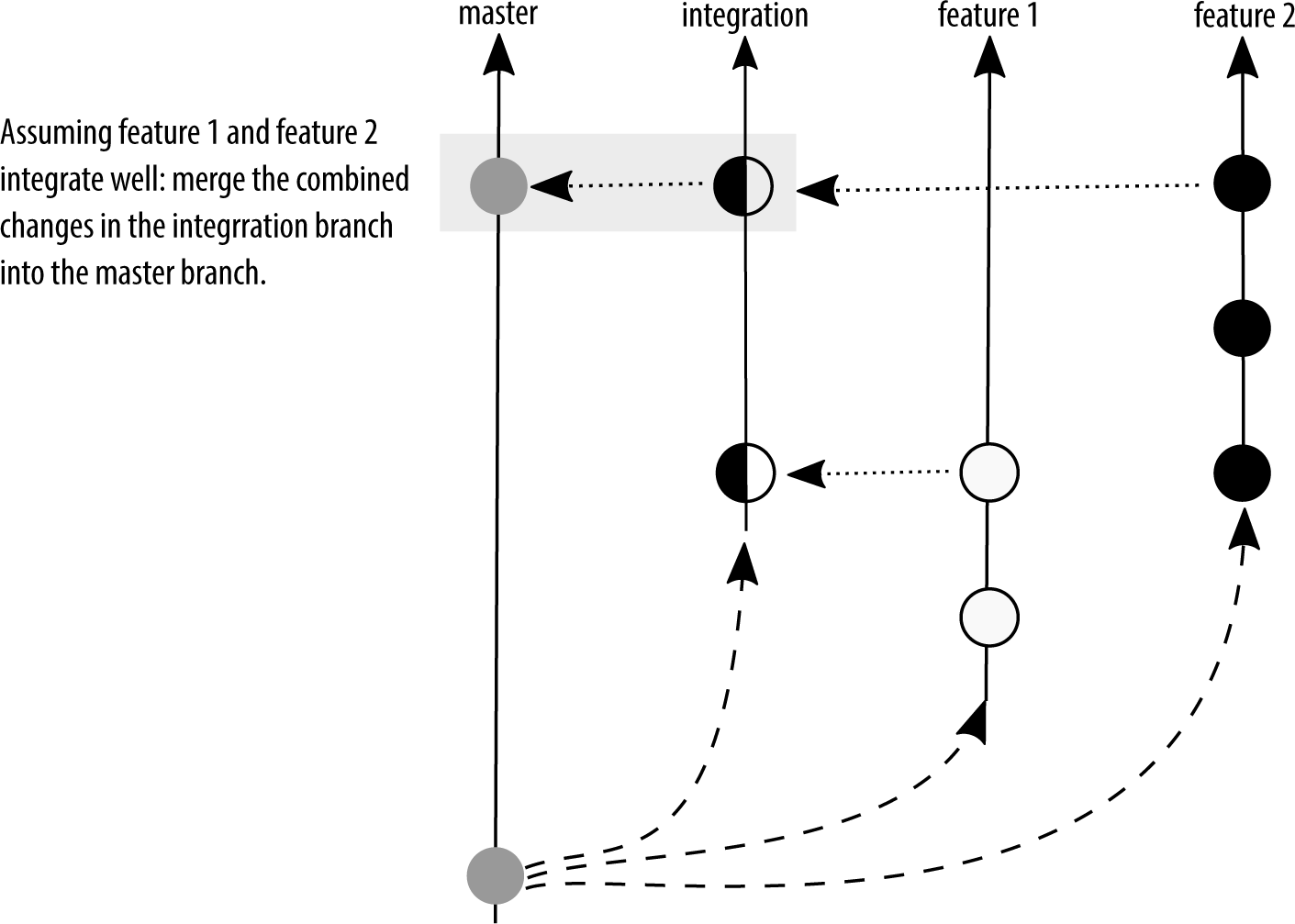
branching strategies: feature branches
Downsides?
Maintainance overhead if not merged quickly
branching strategies: feature branches
Advantages?
Allows more experimental features
Facilitates peer review based worflow
branching strategies: state branching
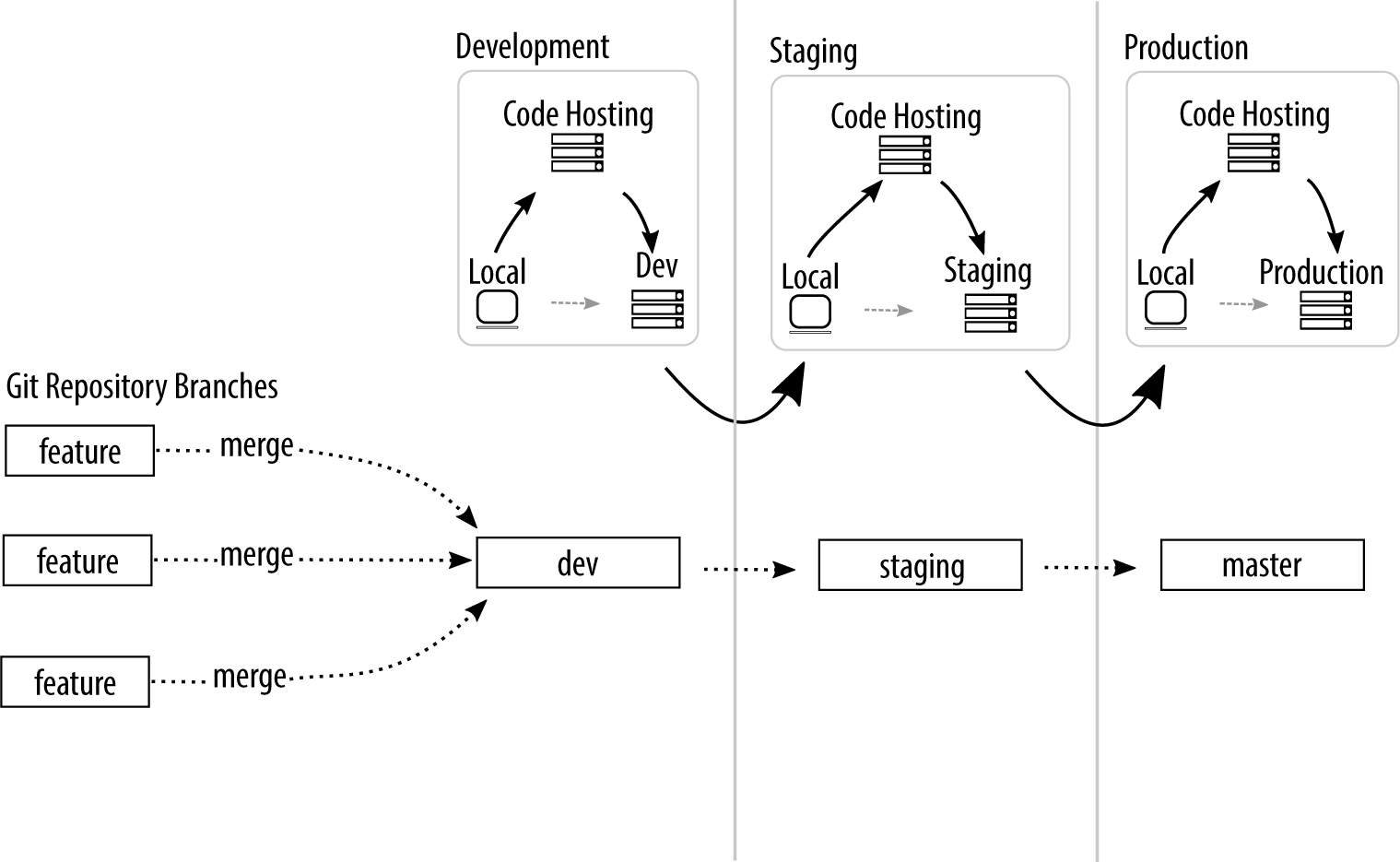

Esp. first 4 and "remote" levels!
We continue the lecture after the break
Workflows
Branching strategy → Workflow
e.g. GitHub Workflow
Workflow → Development Process
e.g. Extreme Programming (XP)
Workflows: Example GitHub Workflow
Feature branches
Peer review
Pull/Merge requests
Workflows: Example GitHub Workflow
- 1. create branch or fork repository
- 2. commit changes
- 3. create pull/merge request
- 4. peer-review pull/merge request
- 5. apply suggested changes
- 6. accept/reject request
- 7. delete branch/fork
Workflows: XP and pair programming
- 1. commit (failing) tests
- 2. commit changes
- 3. run tests
- 4. refactor changes
- 5. push to main
Choosing a worflow
Dependent on socio-technical environment!
Hence, start simple and adapt
git conventions
Conventions: project specific, agreed-upon standrads
- Onboarding
- Misunderstanding
- Reduce conflicts (technical/social)
- Example: variable naming (e.g. camelCase, snake_case)
git conventions
- Enable tooling and automation
- Making expectations explicit
git conventions
Never universal → Negotiation
Each project adapts conventions
<type>[optional scope]: <description>
[optional body]
[optional footer(s)]
EXAMPLE:
feat(api)!: send an email customer when product is shipped
Beyond git conventions
Source code conventions
Automatic Quality Control
→ Adequate code reviews
Source code reviews
- We are all equals
- We are equally able to review
- We want to learn from each other
- Uncover better ways
- Help each other
- Trust each other to get job done
Source code reviews
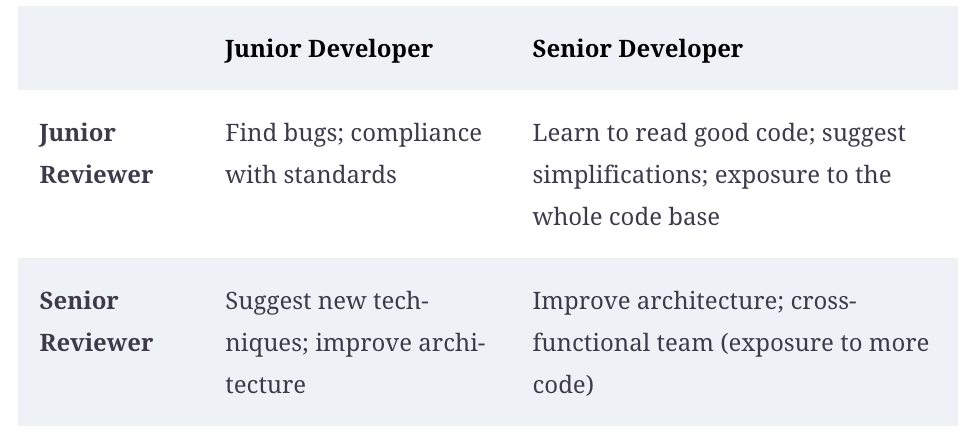
Source code reviews
- 1. Reviewing the goal/task
- 2. Download changes and run them
- 3. Review changes
- 4. Suggest changes & submit review
Source code reviews: Review changes
- 1. Does it wok?
- 2. Does it follow best practices?
- 3. Would I have done it differently?
- 4. What did I like/learn?
Use conventions and tools to minimize 2 and 3!
Focus on 1 and 4
Automating reviews: Code linters
Automating reviews: Code linters
Using tools allows us to focus on more important stuff
Automating reviews: Code formatting
PEP-8 style guide
"A style guide is about consistency"
Automating reviews: Code formatting
"A style guide is about consistency"
Use a tool instead!
Automating reviews: Code formatting
Automating reviews: Code formatting
Automating reviews: Code formatting
Adding meta-information to repository
Here: Development environment configuration
Later (DevOps): Infrastructure, testing and deployment configuration
Source code reviews: Review changes
- 1. Does it wok?
2. Does it follow best practices?3. Would I have done it differently?- 4. What did I like/learn?
Good conventions support automation
Bad conventions introduce opinions and conflict

Code review should have a mutual benefit
Missing in the above: a senior needs to learn how team members think and feel
Source code reviews
- We are all equals
- We are equally able to review
- We want to learn from each other
- Uncover better ways
- Help each other
- Trust each other to get job done